![]()
![]()
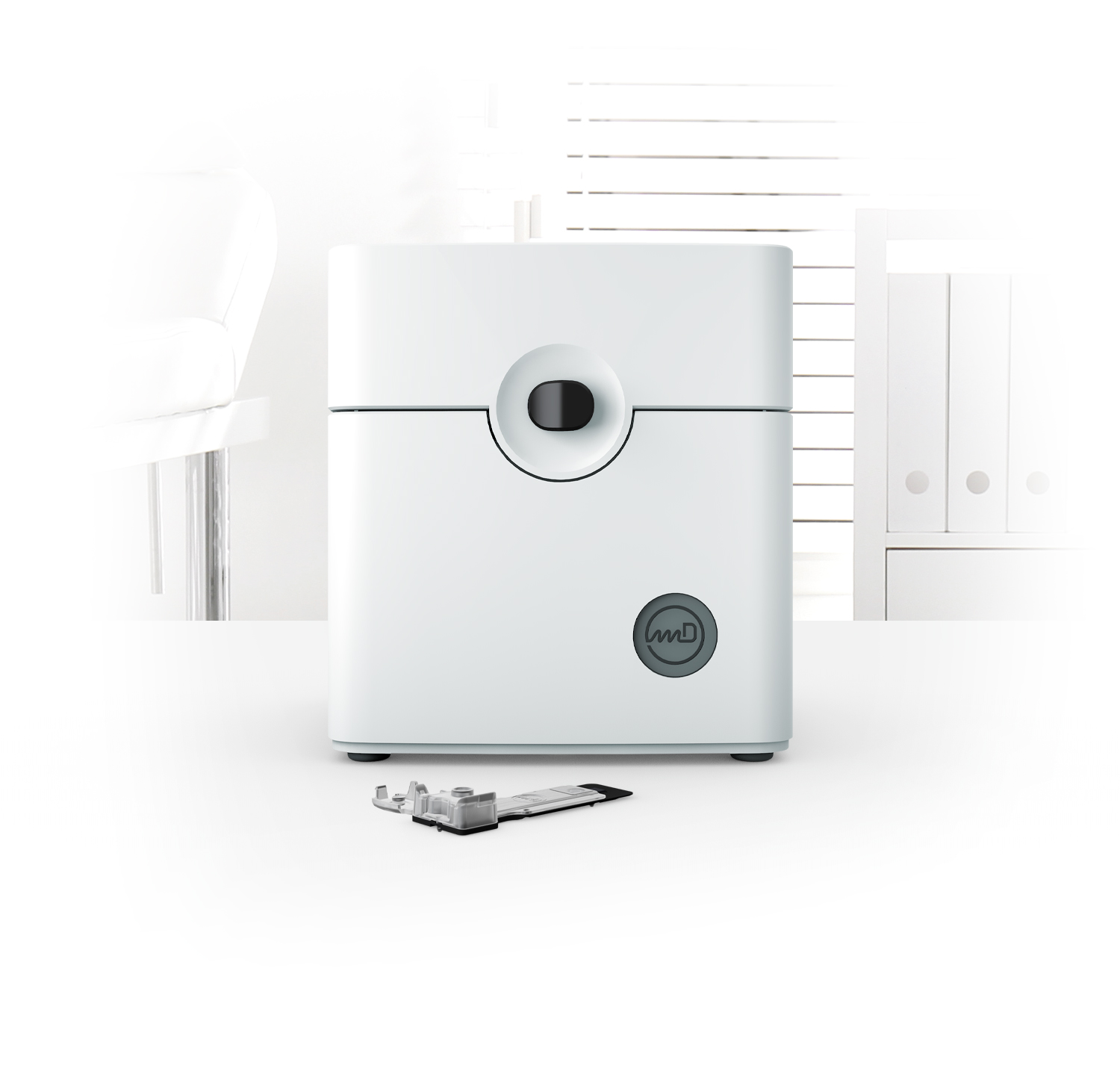

Reader Dimensions: 7 x 7 x 7 inches
nanoFluidic Processor
At the heart of miDiagnostics’ technology is a nanoFluidic Processor (nFP), designed to allow for high-precision, fast test results and enabling widespread use at a low cost.
Production of this next-generation technology can be scaled up at speed, depending on the demand, due to the use of existing, standard silicon chip manufacturing processes.
The miniaturized processor on a silicon chip houses a network of microchannels, made with nanometer precision. These channels enable fluidic operations such as pumping, valving, mixing, and volume metering.
Various diagnostic tests can be performed on fluids which are guided through the system by capillary forces and can redirect liquids, even reversing their direction. In addition to high precision liquid control, the silicon chip enables ultra-fast PCR, allowing virtually any biomarker to be processed: from cells and small molecules to proteins and nucleic acids.
It was initially developed by imec, the world-leading R&D and innovation hub, with the expertise of Johns Hopkins University, the leading US research and medical centre.
How it works.

Silicon nFP
Silicon chip processes a small sample via a miniaturised network of channels and enable ultra-fast PCR.

Test Card
Small processed sample loaded onto the disposable test card embedded with a silicon chip.

Reader
The reader with small footprint reads the PCR Card and performs ultra-fast thermocycling and optical detection.
“miDiagnostics has the potential to disrupt and transform the industry by making diagnostic information available to clinician and patient alike.”
“Its easy-to-use and cost-efficient test will revolutionize point-of-care testing by directly engaging with patients and enabling speedy intervention.”
“Proud to be leading a top team and together with our numerous partners to make a significant contribution to healthcare in general.”
“As a Non-Executive Director on miDiagnostics’ Board, I have been privileged to witness its continued development. I am very proud to see many years of hard work coming to fruition and providing value, facilitating the return to a normal way of life, with potential to move high quality testing closer to the patient.”
“This technology could aid the management of outbreaks in challenging settings, such as nursing homes and home care environments, allowing healthcare professionals to adjust their management decisions at the point of care. ”